Articulating impact can be a daunting challenge for investors however there are a number of great tools available to help. There are a number of impact reporting tools and frameworks to help with this process.

UN Sustainable Development Goals (website)
The most common, and best known framework, for impact is the UN sustainable development goals. These are a set of 17 goals which cover: no poverty, zero hunger, good health & well-being, quality education, gender equality, clean water & sanitation, affordable & clean energy, decent work & economic growth, industry, innovation & infrastructure, reduced inequality, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, life below water, life on land, peace, justice and strong institutions and partnership for the goals.

Doughnut economics (website)
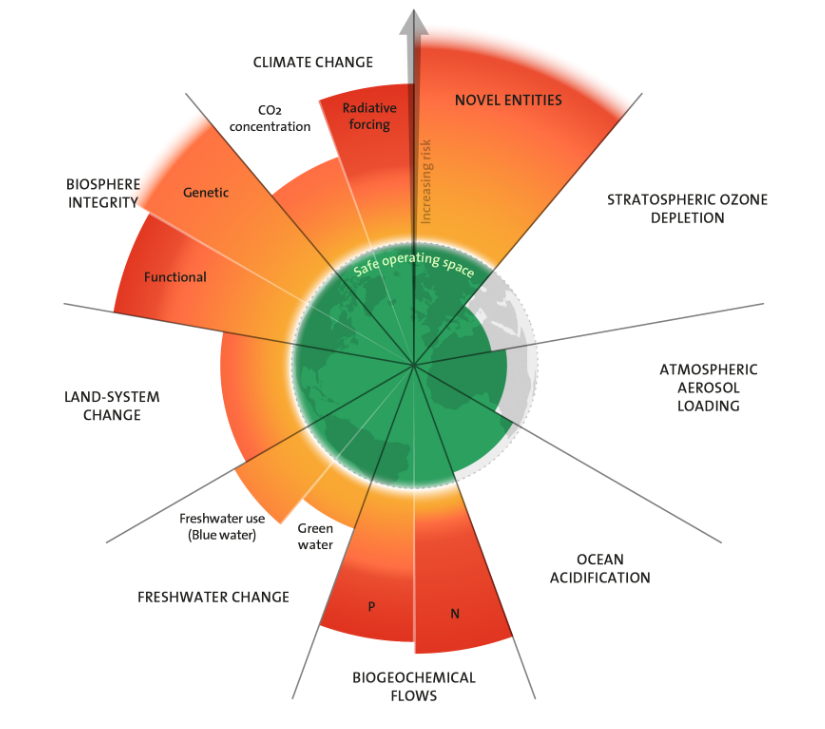
Kate Raworth proposed a solution based around the concept of "doughnut economics". The environmental ceiling consists of nine planetary boundaries, as set out by Rockstrom et al, beyond which lie unacceptable environmental degradation and potential tipping points in Earth systems. The twelve dimensions of the social foundation are derived from internationally agreed minimum social standards, as identified by the world’s governments in the Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. Between social and planetary boundaries lies an environmentally safe and socially just space in which humanity can thrive.

UNEP Impact Radar (website)
The Impact Radar offers a holistic set of Impact Areas and Impact Topics across the three pillars of sustainable development (economic, environmental and social), which can be used by private finance and business to understand and manage positive and negative impacts across the three pillars. The Impact Areas and Topics are defined based on internationally recognized standards and definitions, including the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

The key dimensions of the UNEP Impact Radar are:
Social: integrity and security of a person (conflict, modern slavery, child labor, data privacy, natural disasters), health and safety, accessibility (water, food, housing, healthcare & sanitation, education, energy, mobility, information, connectivity, culture & heritage, finance), livelihood (employment, wages, social protection), and equality and justice (gender equality, ethnic / racial equality, age discrimination, other vulnerable groups)
Socio-economic: strong institutions (civil liberties, rule of law), healthy economies (sector diversity, flourishing MSMEs), infrastructure, and convergence
Natural environment: climate stability, biodiversity & ecosystems (waterbodies, air, soil, species, habitat), circularity (resource intensity, waste)
Impact Cubed (website)
Impact cubed provides powerful impact data for analysis, reporting and portfolio construction. They provide institutional investors the factual granularity they need to analyse impact and create leading sustainable products. They use a metric across the following dimensions: carbon efficiency, scope 3 carbon efficiency, waste efficiency, water efficiency, gender equality, executive pay, board independence, environmental good, social good, environmental harm, social harm, economic development, avoiding water scarcity, employment, and tax gap.

Stockholm Resilience Center (link)
From global warming to the biosphere and deforestation, from pollutants and plastic to nitrogen cycles and freshwater: Six of nine planetary boundaries are being crossed, while simultaneously pressure in all boundary processes is increasing, new research published in the journal Science Advances shows.
EU Taxonomy Alignment
Another interesting area is the EU taxonomy alignment


Comments